HAN, Jan 1, MECHLOVA, Erika2, DVORAK, Leos3, EDL, Milan4 & KONICEK, Libor5
1
2 University of Ostrava, Ostrava, erika.mechlova@osu.cz
3 Charles University, Prague, Dvorakl@otokar.troja.mff.cuni.cz
4 University of West Bohemia, Pilsen, edl@kpv.zcu.cz
5 University of Ostrava, Ostrava, libor.konicek@osu.cz
Abstract: The conference presentation is oriented to a description of both goals and possibilities of multimedia and simulation utilise in educational software oriented especially to the field of students and employees training.
In an introduction authors make reference to a role and an importance of creationism in education in relation to an information society arrival. Strong tool of student’s preparation into this society, which would have to support primarily students creative thinking and self-expression, is based on special systems modelling and simulation. Modelling of special system leads to good understanding of system elements, relationships and its functionality. Simulation of this system leads to a consciousness of decision implications.
The manner of information presentation is taken as an important factor of educational software effectiveness. In this field is referred to a possibility of effective position of multimedia communication way. This style includes animations, which is a powerful tool of expression, videos, audio sequences, pictures etc.
By interconnection of modelling, simulation and multimedia elements (with a strength deal of animations) to a particularly oriented educational software arises strong tool for computer aided education especially for training.
Several training applications are shown in the presentation that is connecting simulation and multimedia in particularly oriented expert’s fields. There are shortly described especially programs there: the Manager game Business Management is focused on a decision training in business processes; the Simulator of Order Progress through a Workroom is focused on a decision training in process of productive order progress. In the last part of contribution the information about the developing the Multimedia Encyclopaedia of Physics are presented. All these applications were developed at the Department of Industrial Engineering and Management – the University of West Bohemia.
Keywords: Multimedia, Modelling, Simulation, Computer Aided Education, Learning, Training, Courseware
One of the hot problems of information society arrival is a people nurture and education into such form, so that they can both fully live in information society and further develop it. Among important skills, which a successful member of society should have, belong especially: the ability of creative thinking, team-task solving, system of thinking, the ability of both gaining and distributing correct information in correct time and place, to utilise advantages of modern information technology, the ability to accept full responsibility for his or her decision, a promptness to insist studying new things etc. Educational system should accept and utilise methods of preparing an individual in harmony with the mentioned requirements.
Constructivism gives answers to these needs. Ideas of constructivism are in accord with modern knowledge of cognitive psychology that concern of the dynamic structure of synapses. Among aims of constructivism are: motivate students to learning, to activity in solving special situation that means to give them opportunity to understand connections between knowledge and to develop conditions for team task-solving.
Information and communication technology (ICT) plays serious role in constuctivistic education. ICT helps in creation of problem situations that demands activity of students in solving – modelling and simulation. ICT gives instruments for understanding of information and for enhancing of motivation of students – multimedia. ICT creates environment for team solving tasks – Internet. ICT is means of quick receiving of information – Internet and elaboration of information to asking shape - software application.
The using of multimedia educational software is one form of using modern information educational technology in the educational system. The educational software is the software with a structure and a content by that user is led to receive a new knowledge, skills and customs from the special field by the modern didactical methods. The multimedia educational software is used not only by academic institutions but by companies, too. It helps to requalification of employees and in courses of new methods and technology etc.
We can divide the multimedia educational software according to its function in an educational process. This function defines whether the educational software intends to adopt or evaluate the knowledge. The educational software is divide according to its function into three categories:
Modern information technology gives to the educational software the means of realisation of its functions (learning, training, and evaluation). Multimedia, simulation and modelling are these means.
The educational software cannot give all functions in every case. For example the software of the Encyclopaedia of Physics belongs to the software supporting learning. It is intended to give knowledge and includes the multimedia components that represent an information in convenient form. A simulation is not typical in this case but is use for the explanation of more complicated problems and for an attraction of encyclopaedia (e. g. additional game). Modelling is not typical element in this case, too. A modelling supports an attraction and a fun of application but not its main function.
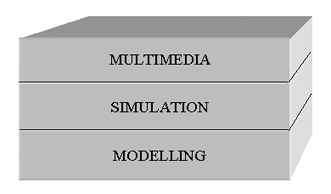
The software supporting training has another intention. The special training software demands the components for fulfil of main purpose. We can say that each of following component fulfils its role during training – multimedia, simulation and modelling.

Figure 1. Components of training software
The modelling educational software gives students the instruments for the construction a model of real world. The model offers students the understanding structure and its elements, connections and functions of connections for the explaining behaviour of this world. The thinking of student is deepening during understanding of world by self realisation. The student comes from real world and from his experience and knowledge of real world. Student gives names these knowledge and experience during modelling. Afterwards student creates the model of a real world by using available instruments. The computer model of a real world is not only model but this model concludes the mental model of a student thinking.
The modelling is the first stage of creative cognition of a special system or a phenomenon. The simulation follows the modelling and this simulation uses model that was created before.
The simulation deals with development of a level of understanding of a part of system and whole system. The simulation consists of a manipulation with the model of a special system in space and time on that student can understand regularity of system that cannot be understand in real space and time.
Better understanding of the special system is the reason of the simulation using in an educational process more and more. The explanation of some concepts, relations and processes is clear by the means of simulation to compare with a long explanation by words. The computer simulation is an opportunity to explain some of real processes to student easy way. There are experiments that cannot be made out in real space and real time there. There is the computer simulation of those experiments. The computer simulation is used for training and a verification of knowledge about a special phenomenon.
Skills and skills training are the second domain of the computer simulation. The software supporting training is used by school institutions and company system for education of employees. The user can understand positive and negative consequences of the solving situation by the simulation of the situation of special model under special conditions. The operation with model gives intended answers on many questions. This principle is used in the management games – especially in the ”Business Management” (Part 3), in the simulators of the logistic processes – especially in the ”Simulator of Order Progress through a Workroom” (Part 4) etc.
We can see higher effect of the simulation if the modelling of this system proceeds. And the multimedia offers very effective presentation of the resulting data from simulation.
The multimedia is the component of the educational software that create ”surface” of the software and under this surface are hidden the educational methods that use the modelling and the simulation. The multimedia gives a proper presentation of information by above-mentioned methods. The multimedia presentation gives information in a form of video sequences, animations, sounds, pictures and texts. The interaction of a student with the computer technique has multi sensuous dimension from this point of view.
The multimedia information is for students better intelligible than the only verbal information. The multimedia information has a form as information those a student gains by a natural perceiving of a world. The student is more open to information that has a natural form for him. From this natural form follows a higher effectively teaching-learning process trough motivation.
The examples of the educational software are presented in the following parts of contribution. This software was developed at the Department of Industrial Engineering and Management at the University of West Bohemia in Pilsen.
The manager game Business Management is the educational software that belongs to the field of the computer based training. The game is oriented to the field of investment and business processes of a company. The game simulates the activities combined with a develop of company. The undertaking is based on a special product production introducing and selling of this product on the different markets. Since the consequences of simulated solutions have not any impact on a real situation in a company, the managers can try the different variants of their decision and to analyse the decision consequences. In this way they obtain valuable knowledge they can utilise in their practice later.
The game participants behave as the company managers. Their tasks are to develop the process of undertaking with the help of a fundamental capital. The firm acts in a market environment and its products are met with the competitive products of the other firms on the market.
Players are deciding in the three basic fields during the game:
Field of production
Field of sale
Field of financing and company economy
The goals of game participants are:
The game the Business Management has a local character. Every running game works with one set of data. All data are saved into database continuously within the game. The processing of data flows within the game is shown on the figure 2.
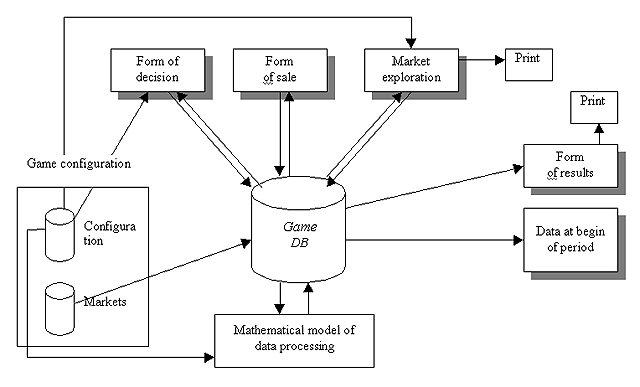
Figure 2. Data flows of Business Management software
The company managers are the target group of the game. These are focused on economy, business and strategic management. Good knowledge of informatics is not assumed for this target group. The user environment was developed so these users could not be bothered from the point of complicated control and by a inconvenient content. The user environment motivates the users and it holds their attention.
Characteristics
The simplicity and the arrangement of the game user environment is provided by the standard way of a control that is typical for classical applications of Windows. The most frequent used control elements are completed by the colour graphical symbols with its functions.
Arrangement, level of interactivity and information conveying of the game are strengthened by the use of multimedia technology (video, audio, picture). For example the playing audio sequences in the game fulfil a purpose of: accompanying some actions (button press, form show …), setting the atmosphere of some state (game starting, bankruptcy …) and holder of information (commentary in a game quick tour …). The game help is, apart from other things, created as a video presenting a manner of a game control and its basic rules. The particular forms are completed by the pictures symbolising a sense of given form etc. The user environment with a multimedia presentation of information has the motivating role apart from other things.
Since various enterprises have different value indicator (e.g. material costs, expenses of for wages, expenses of energy, structure of fixed expenses, initial capital, prise and capacity of production lines etc.) and they trade at different markets with specific demands, competitive offers etc., it was necessary to make the game with such parameters to be suitable for wide spectrum of industrial enterprises. The control of these game parameters is provided by application Business Management Service.
The structure of Business Management Service application consists of two areas. The first area is determined for the firm parameters setting. Second area makes possibility to specify a character of different markets, on which the firm will trade.
The provider of the game, who knows a program access password, has an access to particular parameters setting.
The Simulator of Order Progress through a Workroom is software determined to support a micrologistic decision making. This software comes under the field of educational software oriented to training support. Its development is a part of solving of the national grant: ”Innovation of courses of the Logistic of production system”. The simulator is based on the model of production system and it enables to make the simulation experiments with a number of system input parameters.
The simulator is determined to a simulation of the workroom production system. Two type of products are manufactured in this workroom. The bills of material of these products are specified. The production technology of these products is prepared for five professions with a limitation of maximum workers (for each profession 12 workers maximally). These professions are turner, milling cutter worker, rubber, locksmith and fitter. The performance standards of particular product elements are entered in the model. There is three-shift operation in this company. The transfer periods of materials and products depend on a speed of transport and a traffic road length (entered in the model). The model respects a hourly costs of work at different workplaces and an input price of different intermediate products.
The training of simulator users leads to assumption of some skills from a field of production system control on the tactical and operative level. The goal of the simulation is: e.g. to find least number of workers so that the production could be performed within one month, to reduce a production lead time, to find suitable transfer batch etc. Minimum product costs have to be reached, too.
The users of simulation realised the consequences of their decision after the finishing of several experiments with a various simulation values. It leads to higher quality of their next decisions.
The multimedia data presentation from the experiment was taken out with the animation sequences in a grate scale. It leads to easier understanding of the simulated processes and to change of a behaviour whole system of the workplace subsequently.
The Multimedia Encyclopaedia of Physics is the educational software that is in a developing stage in the frame of grant Czech Grant Agency 406/98/0975. This software will be ready in the beginning of the 2001-year.
The aims of encyclopaedia are to give the means for individual access to students to study problems of physics on the level of university introductory courses of physics. The subject matter of physics is given in a form of hierarchic structure of parts of special texts accompanied by tables, pictures, animations, video, and audio commentaries. The application provides many additional functions for the learning process.
The subject matter is divided into fourteen parts: History of Physics, Common Concepts of Physics (with mathematical background and measurement), Mechanics, Molecular Physics and Thermodynamics, Electricity and Magnetism, Optics, Physics of Microworld, Solid State Physics, Theory of Relativity, Statistical Physics, Biophysics, Geophysics, Meteorology, Astronomy.
The Multimedia Encyclopaedia of Physics belongs to the software supporting learning.
The development of the multimedia educational software supporting learning, training and evaluation and its implementation to educational systems of schools and companies are in relative bad situation in the Czech Republic in this time.
The development and the implementation of the educational software in Czech schools is a bit worse to compare with west countries. The special encyclopaedias are created for supporting school education in Czech republic but many of its are only translations from foreign languages. The interest is given to the compulsory subjects at secondary schools, respective to the learning of languages. The development of the educational software on university level courses is exception, but some teachers produced materials for support their courses. The large system with structure and organisation is missing in practise.
The development of the multimedia educational software for the supporting company education is in worse situation in the Czech Republic in this time. A lot of companies have problems with using of modern computer technique in basic fields of its activities and these aids are not used in education of employees. The mapping of using information technology was carried out in some companies in West Bohemia region and results were not favourable. There are only a few institutions for the development and the implementation of an educational software for companies there.
[1] BRDICKA, B. Uceni s pocitacem. Praha: PrF UK, 1996
[2] BRDICKA, B. Vliv technologii na rozvoj lidskeho mysleni. www, 1998, Available from: http://omicron.felk.cvut.cz/cgi-bin/charset/~bobr/vlivtnam.html?charset=CP1250
[2] COVER, J. Introduction to System Dynamics. Powersim Press, 1996
[3] FLOYD, S. The IBM Multimedia Handbook. NY: Brady Publishing, 1991
[4] HAN, J. Vyvoj multimedialnich aplikaci se zamerenim na pocitacovou podporu vzdelavani. Rigorozni prace, Plzen: ZCU, 1999
[5] HAN, J., VOTAVA, V. Pocitacova podpora vzdelavani na vysokych skolach. In: Zvysovani ziskovosti prumyslovych podniku strategickym vyuzitim vyhod IT. Plzen: ZCU, 1998
[6] HAN, J. Vypocetni technika v informacni spolecnosti. In Filosofie, veda, vzdelani. Plzen: ZCU, 1999
[7] HAN, J., VOTAVA, V., SYKORA, M., DVORAK, P. Multimedia v CIM. Plzen: ZCU, 1998
[8] HORVATH, G., HAN, J., ULRYCH, Z. Inovace programu cviceni z predmetu Logistika vyrobnich systemu. Plzen: ZCU, 1999
[9] MECHLOVA, E. The True Experiments or Simulations? In New Ways of Teaching Physics. Ljubljana: Board of Education, 1997. ISBN 961-234-051-X.
[10] PETTY,G. Moderni vyucovani. Praha: Portal, 1996